Sales techniques
Here you’ll find most of today’s sales techniques, with their advantages and disadvantages, and the context in which they should be used. SONCAS and SONCASE The SONCAS is the best-known system in the French-speaking world, having trained several generations of salespeople, and is now joined by E d’Écologie. Benefits Disadvantages SICSIC Benefits Disadvantages SEC The […]
Here you’ll find most of today’s sales techniques, with their advantages and disadvantages, and the context in which they should be used.
SONCAS and SONCASE

The SONCAS is the best-known system in the French-speaking world, having trained several generations of salespeople, and is now joined by E d’Écologie.
Benefits
- With just 6 letters, it categorizes all the psychological motivations behind a customer’s purchase. We can buy millions of products or services, but they all respond to just 6 motivations.
- The system allows the salesperson to discover which advantages to use in his sales pitch.
- Soncas can be applied in combination with other techniques such as SOS or CAB.
Disadvantages
- Some salespeople find that 7 motivations are too many, because there’s a lot to think about in a sale. In this case, you can use the SEC method described below.
SICSIC
- Safety
- Comfort
- Interest
- Sentiment
- Innovation
- Consideration
Benefits
- A technique similar to SONCAS, it can also be used to categorize any purchase into 6 categories in order to adjust the sales pitch to the purchase.
Disadvantages
- Less well known than Soncas, it is also less precise: the notion of interest is vague and can apply to several different motivations.
SEC

The SEC sales method is a simplification of SONCAS to make salespeople’s work easier:
- Security: need for protection or need to save money
- Ego: the need to look good, or to achieve self-fulfilment through ecology
- Convenience, comfort, or sympathy for the product or seller (last S in Soncas)
Benefits
- With three letters, it combines the 6 or 7 motivations of the other techniques.
- It’s the simplest and the most popular among salespeople who use it.
Disadvantages
- Less specific than SONCAS
SPIN
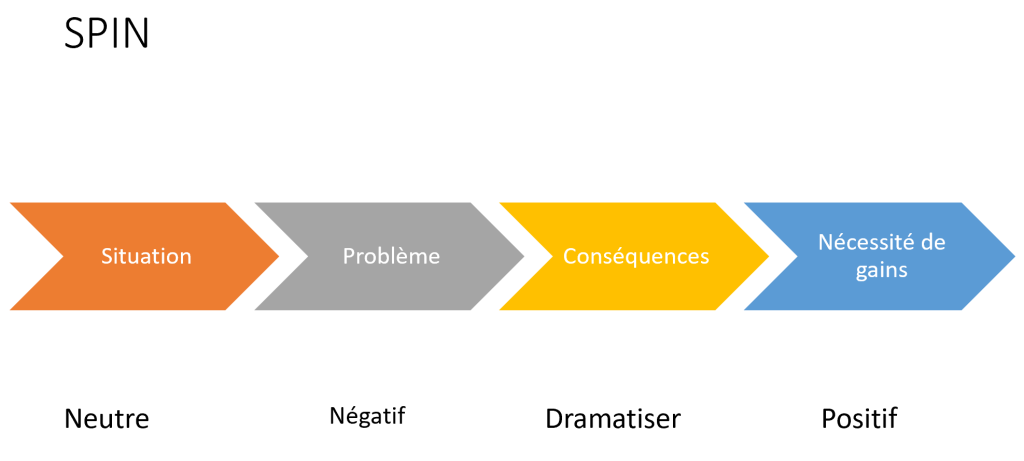
- Customer situation, economic situation, real-life situation
- Problem: difficulties experienced by the customer
- Involvement: consequences of these problems on a personal level, we push as far as we can
- Needs payoff
Benefits
- The SPIN sales technique is the best-known in North America, and tests have shown that using it increases sales.
Disadvantages
- It’s a little dated now
- Focusing on the “boo-boo” and its personal consequences, turning the knife in the wound, leads to major rejection reactions on the part of some customers. The SOS technique avoids this pitfall and also plays on the customer’s dream.
PSAI
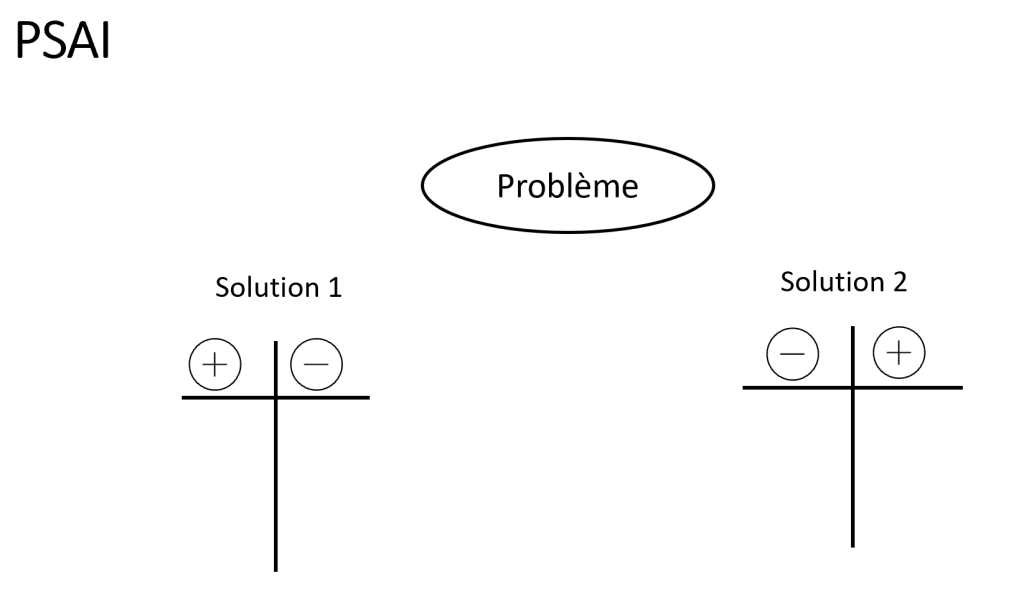
- Problem
- Solution
- Benefits
- Disadvantages
I learned it from Bernard Julhiet in the 90s. It’s a technique similar to SPIN, which focuses on the problem and its solutions, with their advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits
- It’s a technique that subtly encourages customers to choose the best solution for themselves. Correct use of the technique influences the choice of interlocutor, the first solution is the customer’s current one, or the competition’s, and we end with our solution and its advantages, which the customer remembers best.
Disadvantages
- Here, too, the focus is on the problem, which can irritate customers with strong egos who can’t admit that they may have made bad choices in the past.
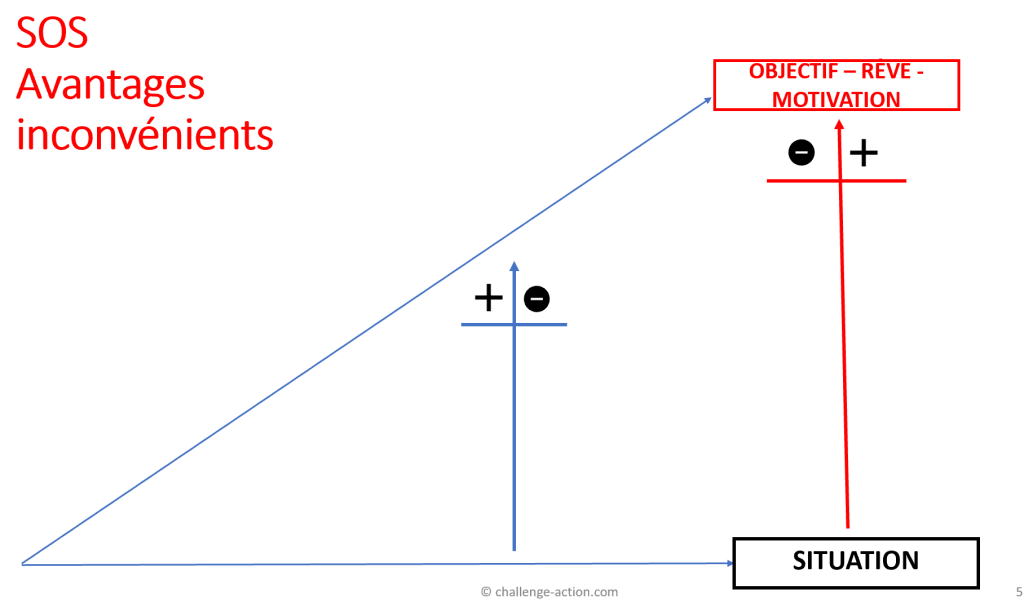
SOS
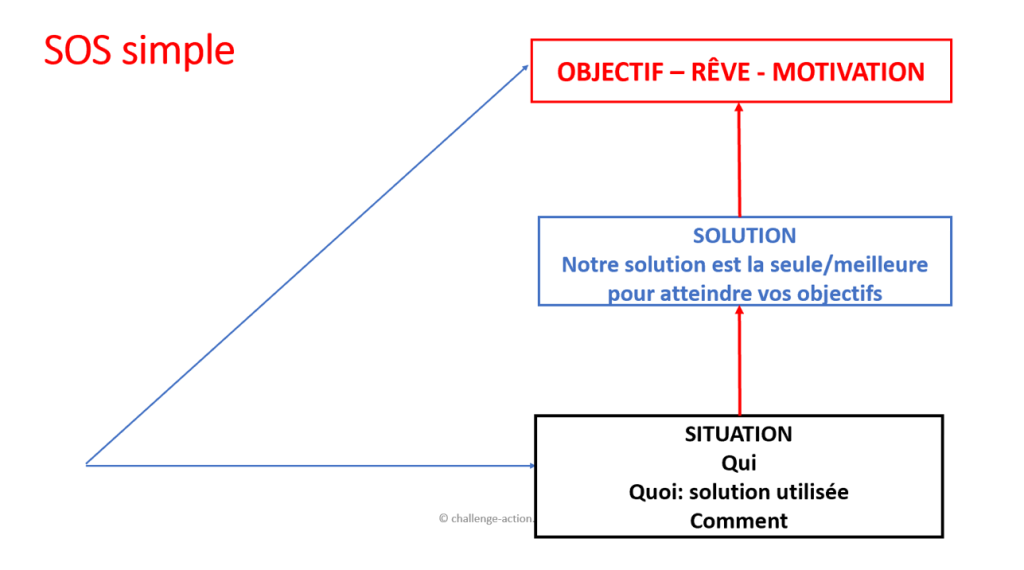
The SOS sales technique has three phases:
- Current customer situation
- Goal, dream, project or motivation
- Solution: our solution
Benefits
- It’s a product or service sales technique I’ve developed to get around the drawbacks of SPIN and PSAI, which focus too much on the negative aspect of the customer’s current situation. In fact, the definition of a problem is a gap between a current situation and a desired situation, so we can get the customer to describe his or her situation in a neutral way. This situation will only become a problem when the customer admits that he or she wants something better. The focus is on your goals, i.e. your dreams.
- Selling is also about offering your customer something to dream about!
- I’ve applied it in hundreds of companies, and the results are always spectacular when properly applied.
- SOS works equally well in B2B and B2C markets
- SONCAS, SICSIC or SEC motivations combine harmoniously with the technique
Disadvantages
- The method requires a thorough knowledge of the situation and objective issues that will lead to the emergence of a current problem and then a dream for the customer.
- It’s an intelligent method that requires a logical sequence of questions to lead to a sale.
SOS Global solution
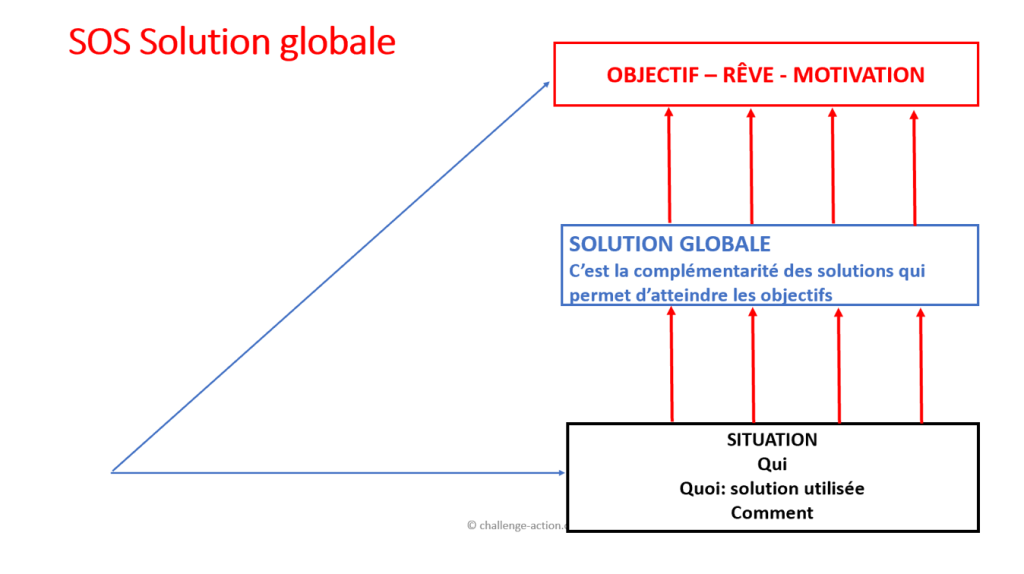
The SOS global solution offers the customer a complete and ideal solution, including several products or services.
- Customer situation
- Goal, dream
- Comprehensive solution of complementary products tailored to customer objectives
Benefits
- An intelligent method of cross-selling or upselling based on an understanding of the customer’s needs and combining the products or services sold to create a comprehensive solution that stands on its own.
- It’s easier to sell an advantageous overall solution that holds together than to sell one product, then another, then a service, as in cross-selling.
- The idea is not to sell for more, but to offer a better overall solution.
- The salesperson becomes the expert the customer trusts
- If the solution is too expensive for the customer, we can ask them what they prioritize and want to keep among the various products on offer.
Disadvantages
- The salesperson must have a thorough knowledge of his company’s entire offering
- Sales techniques must be mastered, and the salesperson must wait until he or she knows enough before proposing a global solution.
CROSS-SELLING
- Cross-selling is based on the fact that the sale of one product leads to the sale of another complementary product, and so on.
Benefits
- Leads the salesperson to sell more than the customer is initially looking for, thus increasing the invoice. It’s especially effective in-store or in sit-down sales, when the customer calls or comes into the store to buy a product.
Disadvantages
- Sometimes a mechanical process, less intelligent than selling a global solution.
- Above all, the salesperson appears to be putting pressure on himself by constantly trying to sell a complementary product.
- The SOS Global Solution is more complex, but far more effective and qualitative.
Upselling

- The sale of a more expensive, higher-end product than the one initially sought by the customer.
Benefits
- The salesperson increases sales and the customer leaves satisfied with a higher-quality purchase.
Disadvantages
- Effective for certain products, such as cars, beauty creams and insurance, but still rather basic and transparently pushes customers to spend more than they originally wanted. The sales rep can be seen as pressure selling, the SOS Global Solution is better.
SOSAI
- Situation
- Objective
- Solution
- Benefits
- Disadvantages
Benefits
- Derived from the SOS technique, it has the advantage of taking the competition’s solutions into account.
- We can let customers choose for themselves, while influencing their choice.
- Our solution is, of course, the last one we talk about and end with the benefits, because that’s what he’ll remember best.
- The most effective technique in competitive situations
- Intuitive technique that does not require comparisons with matrices
Disadvantages
- Salespeople need to know their competition and their weaknesses
- He must be perfectly trained to use the technique for apparent neutrality while subtly influencing the customer’s choice.
SOS comparison
The best technique in a competitive situation, even better than SOSAI, is a little more complicated, and is described in our online course on sales techniques.
CAP

CAP is a simple, product-focused sales technique.
- Features
- Benefits
- Evidence
Benefits
- A very simple technique to use when selling a product repeatedly. Proof is used to convince skeptical customers of the benefits. It’s perfect for selling products in-store, at trade shows and fairs.
Disadvantages
- Technique that doesn’t necessarily take customer needs into account and doesn’t work for complex products.
CAB

CAB is a simple sales technique that focuses on the product, but also on the benefits for the customer.
- Features
- Benefits
- Customer benefits
Benefits
- A simple technique, but more refined than the CAP technique, it differentiates between the product’s generic advantage and the customer’s specific benefit.
- The benefit must be directly linked to what the customer is looking for, which implies discovering motivations through SONCAS or SEC.
Disadvantages
- Too product- or service-based, it puts the product rather than the customer at the center of the sale.
AIDA
- Attention
- Interest
- Desire
- Acquisition
Benefits
- The technique focuses on the customer’s psychological progress during the buying process.
- Ideal for in-store sales
Disadvantages
- Understanding the customer’s progress isn’t enough to sell: you need to use a complementary technique.
BANT
- Budget: Does the customer have the necessary budget for the purchase?
- Authority: does he have the power to decide on the purchase?
- Necessity: does he need to make a quick decision?
- Time: what are the steps involved in closing the sale?
Benefits
- Perfect technique for filtering a large number of buyers and focusing on the highest-paying ones as quickly as possible
- Ideal for in-store sales, fairs, exhibitions, when there are lots of potential buyers.
- Can also be adapted to complex B2B sales to avoid wasting time on unattractive customers
Disadvantages
- The technique pays off for the salesperson, as it optimizes his or her time, but it can be to the employer’s detriment.
- This technique is used in call centers, where some agents engage in cherry-picking. To limit its use, managers measure average sales instead of agents’ gross sales.
BEBEDC
- Customer needs
- Stakes: consequences of the decision or status quo for the customer
- Budget: What is the customer’s budget? can he increase it?
- Deadlines: what’s next?
- Who decides?
- Competitors: who are they?
Benefits
- Very similar to BANT, but in French, and with the addition of competition
- Systematic method for assessing customer interest
- Well-suited to automobile sales
Disadvantages
- A method that will offend a sensitive customer or any professional salesperson.
- It’s always tricky to talk about budgets too early.
CCS
- Customer
- Centered
- Service
Benefits
- It’s the opposite of the BANT or CAP method, because it focuses on the customer and the service by asking intelligent questions about their needs and aspirations.
Disadvantages
- The method is good, but less structured and specific than the SOS method
ADAPAC
- Suspect
- Brochure
- Abstract of the solution
- Proposal
- Argumentation
- Conclusion
Benefits
- A good description of the sales process
- The method enables the novice salesperson to easily memorize the structure of the sale
Disadvantages
- Any serious salesperson knows enough about the structure of his or her sale to focus on more effective face-to-face techniques, such as the SOS or SOSAI.
- The method overlooks follow-up, which is an important step in the sales process.
SPANCO
- Suspect: target identified, but not yet contacted
- Prospect: suspect who has been contacted
- Analysis: study of the prospect’s situation in order to make an offer
- Negotiating the offer
- Closing the sale
- Buy order
Benefits
- Global approach, including prospecting
- It offers qualification stages to suit certain CRMs
Disadvantages
- A method for novice sellers, everyone should know these steps and focus on more elaborate techniques
4C
- Contact: get the first few seconds right to create a positive atmosphere
- Knowing: discovering the customer’s needs
- Convincing: proposing the solution
- Closing: closing the sale
Benefits
- A simple way to memorize the main stages of a sale
Disadvantages
- Some steps are missing
- Rudimentary method for novice sellers
SIMAC
- Situation: understanding the different aspects of the customer’s situation and identifying his motivations
- Idea: propose a general idea and its general advantages in relation to your motivations
- Mechanism: demonstrate in a concrete, structured way how the idea can be applied to the customer: who, what, how, why…
- Advantage: list the concrete benefits for the customer
- Conclusion: close the sale
Benefits
- Discovering the customer’s situation at the outset is perfect
- Then you sell a general idea before selling a more precise solution.
Disadvantages
- The procedure is perfect, but longer and more complex than the SOS method.
ICEC
- Identify your contact
- Connecting with customers and their psychology
- Exploring and discovering needs
- Advise on the best solution
Benefits
- Perfect technique for inbound sales
- It’s a technique that focuses on the customer and his or her psychology, the opposite of BANT.
- A professional approach that’s geared to the customer’s best interests, which in turn leads to customer loyalty, which pays off over the long term.
Disadvantages
- The SOS Global Solution technique is sharper for inbound sales, but the two methods complement each other.
DISC
- Dominant (red): this customer wants to achieve his goals, so don’t waste his time with pointless discussions, and show him how he can achieve what he wants.
- Influential (yellow): a friendly customer who likes to chat, so you need to take the time to follow up on his topics of interest.
- Stable (green): introverted, relationship-oriented customer who likes details, taking his time and answering questions.
- Conforming (blue): analytical, insecure, task-oriented person, you need to reassure him and show him that you are right with studies and analyses.
Benefits
- We focus on the customer’s personality rather than their motivations
Disadvantages
- It’s a bit simplistic to classify people into just four types, and that’s not enough for sales: you also need an approach and a technique.
BOBI
- Need
- Objective
- Budget
- Identity
Benefits
- Simple, sequential method: the sales assistant fills in a matrix as he gets to know the customer.
Disadvantages
- It’s sometimes tricky to talk about the budget in the middle of a sale, and the best sellers usually mention the price at the very end.
Elevator Pitch
- Who we are
- What we do
- What are the benefits?
- What are the benefits for the customer of continuing in the sales process?
Benefits
- Rapid sales pitch method, less than sixty seconds, so you can continue with a more serious sales meeting
- Perfect for hooking a prospect at a conference, hotel, formal or informal meeting when time is at a premium.
Disadvantages
- The shorter it is, the better you know your sales pitch.
- Benefits must be adapted to the listener very quickly
- It’s a preliminary step, but not sufficient for the sale
Challenger Sale
The Challenger Sale method identifies 5 types of salespeople and 5 stages.
- There are 5 types of salespeople, including the challenger, who performs well above average.
- Worker
- Lone wolf
- Relationship
- Problem solver
- A challenger who questions everything, he doesn’t hesitate to create tension and confront his customers to change their way of seeing things. He takes advantage of the psychological tension, taking control of the relationship to his advantage. He is self-assured, confident and direct, both with his customers and his superiors.
- There are 5 steps to follow
- Reframe the conversation to bring it back to rationality
- Using emotions in the next phase
- Highlight the benefits that customers are looking for in the long term
- Propose the solution
Benefits
- A much-talked-about fashionable method
- Rational and emotional method
Disadvantages
- Complex, complicated to implement, especially in rapid sales.
Menu vs à la carte
- Discover several customer needs
- First, offer the various à la carte services by adding up the prices of each one
- Wait until the customer thinks it’s too expensive
- Return with an identical or enhanced offer thanks to a promotional or “menu” offer, also known as a package.
Benefits:
- Very effective when applied
Disadvantages
- Identify several needs
- Above all, your organization must have a promotional offer in the form of a package, or “menu of the day”.
- This technique is widely used by cell phone companies offering package deals, but is more difficult for other types of sales.
SNAP dirty
- Simple: an offer that’s easy for customers to understand
- Necessary: by providing priceless value that the customer will never find again, it’s “exceptional”.
- Aligned with customer aspirations
- Priority for the customer’s future well-being, to force the quickest decision possible
Advantages of SNAP sale
- Used by the best salespeople I’ve ever known
- Very effective on the spot
- Excellent for the sale of paintings, objets d’art and rare pieces, it’s always “the exceptional opportunity that will never recur and must be seized immediately”.
Disadvantages
- Not always used transparently and honestly
- It’s the very type of high-pressure sale: you do it once, but rarely do it again.
MEDDIC
- Measurable: to measure the impact of our solution
- Economic: who is the economic decision-maker who will use the figures to calculate profits?
- Decisions: what are the other purchasing decision criteria?
- Deadlines: decision-making stages
- Identify the problem
- Champion: who is the prescriber
Benefits
- Efficient for complex sales and large organizations
Disadvantages
- Complex
- Emphasizes the economic aspect while advocating the evaluation of other decision-making factors, which is somewhat contradictory.
- Very rational and neglects psychological aspects
SBAM
- Smile, because it disarms
- Hello with eye contact, because a glance is worth 10,000 words
- Goodbye
- Thank you
Benefits
- Perfect method for in-store customer service, easy to adopt
Disadvantages
- These are the stages of service, not a sales technique, to which we must add the SOS or CAB.
CROC
- Friendly contact
- Reason for calling the customer to capture his attention
- Main objective of the call
- Conclusion of the call
Benefits
- Excellent for making appointments over the phone
Disadvantages
- Limited to making appointments, sales are then made through face-to-face or virtual meetings.
Objection method
- The method assumes that by answering the customer’s main objections, he’ll end up buying.
Advantage
- Turning every objection into a benefit for the customer
Disadvantage
- In fact, a good salesperson knows few objections; they come at the end of the sale, because the customer wants to feel secure.
- Objections are part of the sales process: it’s better to focus on the customer’s needs than to wait for them to raise objections.
Closing method
- A method that focuses on the techniques used to close the sale rather than on the process.
- It’s all about pressure and getting the deal in return for a discount or a gift.
Advantage
- It is true that every sale must end with an agreement.
- This type of sale is quick
- Suitable for areas that offer promotions or gifts, the technique boils down to “do you want the promotion, yes or no? I’ve seen it successfully applied by an insurance company’s top salesman.
Disadvantage
- Pressure sales
- This method results in a large number of customer cancellations and complaints.
5 B de Kepner
- The right product
- In the right place
- At the right time
- At the right price
- Just the right amount
Benefits
- Merchandising techniques
Disadvantages
- The method does not specify the height at which to place the product, bearing in mind that eye level and gondola headers sell the most.
PVAD
- Place: in the right place
- Visible
- Accessible
- Available
Advantage :
- Simple, effective merchandising
RFM
Customer segmentation and qualification in retail and e-commerce
- Recency of contact: when the customer was last in the store, the more recent the more interesting the customer.
- Frequency of store visits
- Average: the customer’s average shopping basket
Advantage
- Allows you to assess the quality of customers in a store or online store, so you can make them offers or call them back using a CRM.
Disadvantage
- Must be combined with a face-to-face or telephone sales method to be effective.
CRM
Some of them:
- Salesforce: the most popular CRM
- Microsoft Dynamics : the CRM of choice for larger companies
- Hubspot: marketing-oriented CRM
- Sugar CRM : the challenger
- ActionClient: the CRM for small businesses, freelancers and startups
Benefits
- CRMs are in fact tools, but they are necessary for the best application of most of the sales techniques and methods described here.
- They allow you to keep track of data over time, to call customers at the right time, to have the figures to classify customers by interest, and to carry out marketing and promotional campaigns.
Disadvantages
- Many CRMs are criticized by salespeople, who feel they spend more time entering data than selling. Choose a simple CRM, especially if you’re small or medium-sized.
Sales techniques: conclusion
Each of these methods is good, so try the ones that seem to work best for you, and choose the one you’re comfortable with and that gives you results. And above all, don’t hesitate to train or perfect your sales skills– it’s the best investment you can make.
SELL AND HAVE FUN!
Jean-Pierre Mercier
